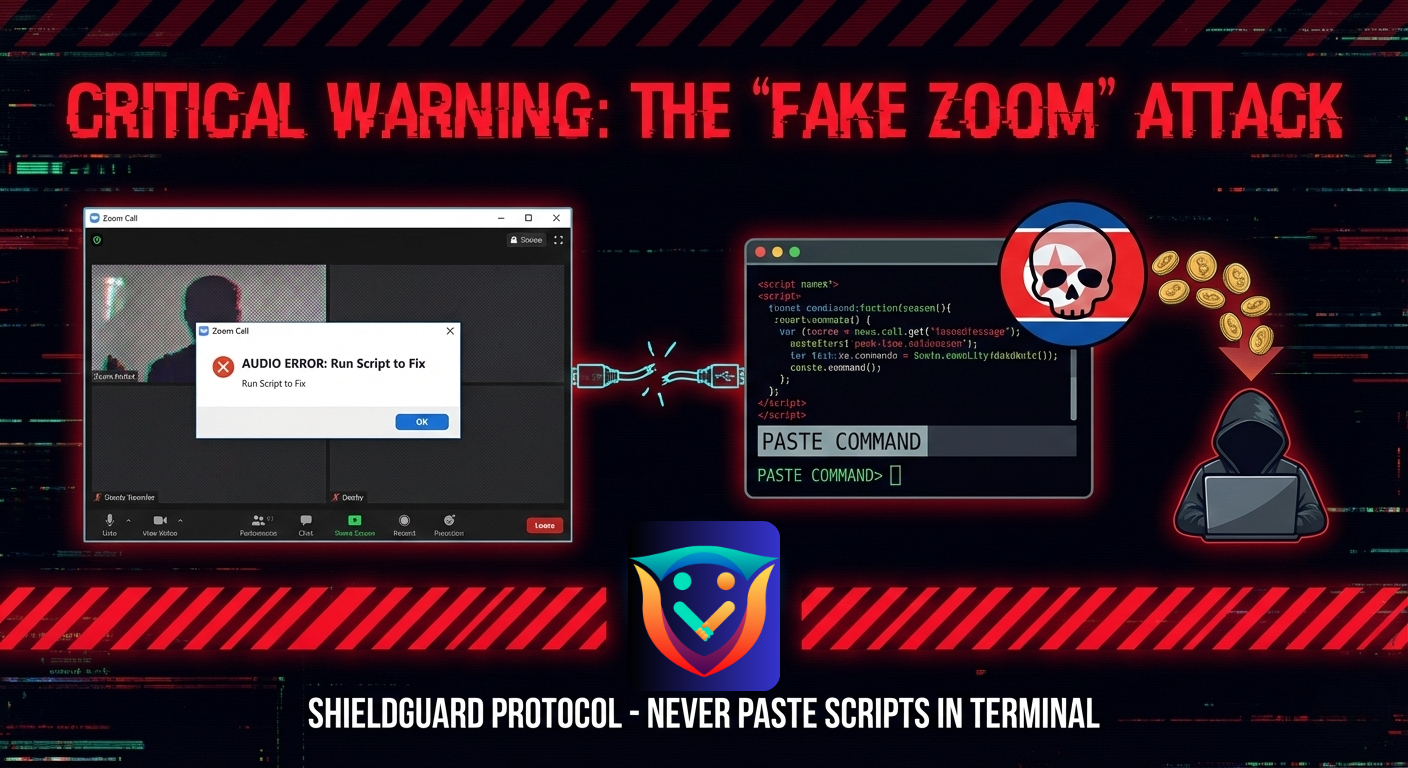
🚨 CRITICAL THREAT: The “Fake Zoom” Malware (North Korean APT)
Severity: Critical (Immediate Wallet Drain / Full System Takeover)
Threat Actor: UNC1069 (North Korea / Lazarus Group Nexus)
First Detected: Late 2024 (Evolved Variants Reported Feb 2026)
Executive Summary
A highly sophisticated social engineering campaign is currently targeting crypto founders, developers, and investors. North Korean threat actors (UNC1069) are impersonating legitimate VCs, podcast hosts, and recruiters to lure victims into a fake Zoom meeting.
Once inside, a “technical glitch” is simulated to trick the victim into running a malicious script. This installs WAVESHAPER and HYPERCALL malware, giving attackers total control over the device to bypass 2FA, steal passwords, and drain wallets.
The Attack Chain: How It Happens
Phase 1: The Lure (Social Engineering)
The attacker contacts you via Telegram, X (Twitter), or Email, posing as a reputable figure.
- The Persona: A venture capitalist wanting to invest, a recruiter with a high-paying job, or a podcast host inviting you for an interview.
- The Hook: They insist on a video call to “discuss the deal.” They send a calendar invite with a Zoom link.
Phase 2: The Glitch (The “ClickFix” Trap)
You click the link to join the meeting.
- The Simulation: The Zoom interface looks real, and you might even see the other participants (often using deepfake video loops).
- The Error: You cannot hear them, or they cannot hear you. A popup appears stating: “Audio Driver Error”, “Microphone Mismatch”, or “DNS Conflict”.
- The Trap: The “Support” window offers a quick fix: “Click here to update audio drivers” or “Paste this code into your terminal to fix the connection.”
Phase 3: The Infection
The moment you run that script or “update,” you are not fixing your audio. You are executing a malicious command (often via PowerShell or Terminal) that downloads:
- WAVESHAPER: A backdoor that creates a silent, persistent connection to the attacker’s server.
- HYPERCALL: A downloader that pulls subsequent payloads, including keyloggers and chrome-extension stealers.
Technical Breakdown: What the Malware Does
Once WAVESHAPER is active, the attacker does not need your seed phrase immediately. They gain:
- Session Hijacking: They steal your active browser cookies (bypassing 2FA for Gmail, Binance, GitHub).
- Clipboard Poisoning: They monitor your clipboard for copied crypto addresses or passwords.
- Keystroke Logging: They record everything you type, including Ledger PINs or passwords.
- Remote Access: They can silently browse your files and look for unencrypted private keys or “seed phrase screenshots.”
🛡️ ShieldGuard Prevention Protocol
If you work in crypto, you are a target. Follow these strict rules:
1. The “Terminal” Rule (Golden Rule)
NEVER, under any circumstances, copy and paste code into your computer’s Terminal (Mac) or PowerShell (Windows) at the request of someone on a call. Legitimate software updates never require you to manually run code.
2. The “Browser-Only” Zoom Habit
Do not use the desktop Zoom client for first-time meetings with strangers.
Action: When joining a link, click “Cancel” on the app launch and select “Join from Your Browser” at the bottom of the page. Browser sandboxing limits the malware’s ability to access your OS.
3. Verify the Meeting Link
Attackers use “typosquatting” domains that look like Zoom:
- ✅ Real:
zoom.us - ❌ Fake:
zoom-meeting.net,zoom-support.com,zoom-v5.io
4. Use a “Burner” Device
For high-risk meetings (unknown VCs or interviews), use a separate laptop or iPad that has zero access to your crypto wallets or main email accounts.
⚠️ What to Do If You Think You Are Infected
If you ran a script from a meeting link:
- Disconnect Immediately: Turn off Wi-Fi and pull the ethernet cable to cut the attacker’s connection.
- Do NOT Login: Do not try to login to your wallet or exchange to “check funds” (you are giving them your password).
- Hard Wipe: The malware persists in the deep system kernel. “Deleting the app” is not enough. You must factory reset the device and wipe the drive.
- Revoke Sessions: From a different, clean device, change all passwords and revoke all active session cookies for email, exchanges, and cloud storage.
- Sweep Funds: If your wallet was on that device, treat it as compromised. Move funds to a new cold wallet immediately using a clean device.
Stay Vigilant. Education is your best defense.
– The ShieldGuard Learn Team